Bulimia Nervosa also more commonly known as Bulimia, is an eating disorder. Bulimia is usually associated with binge-eating and then purging, by purging we mean forced vomiting, excessive exercise, or taking laxatives.
People with bulimia purge or purge-like behaviors display a binge and purge cycle. Purging behaviors also include other methodologies such as fasting, extreme dieting, or extreme exercise.

Such people have unrealistic body standards and are extremely self-critical and sensitive. The most common thing with bulimia is that many patients are either normal weight or overweight which makes it very hard to diagnose.
According to research, roughly 1.5% of women and 0.5% of men will experience bulimia at some point during their life. It is most common in women, and especially common during the teenage and early adult years.
Symptoms of Bulimia
A wide range of symptoms of bulimia display the following:
- long-term fear of gaining weight
- talking about being fat
- preoccupation with weight and body
- a strongly negative self-image
- binge eating
- forceful vomiting
- overuse of laxatives or diuretics
- use of supplements or herbs for weight loss
- excessive exercise
- stained teeth (from stomach acid)
- calluses on the back of the hands
- going to the bathroom immediately after meals
- not eating in front of others
- withdrawal from normal social activities
/signs-and-symptoms-of-bulimia-in-teens-2609258-01-58b75db20fde41f4a0f9e3b440b2688d.png)
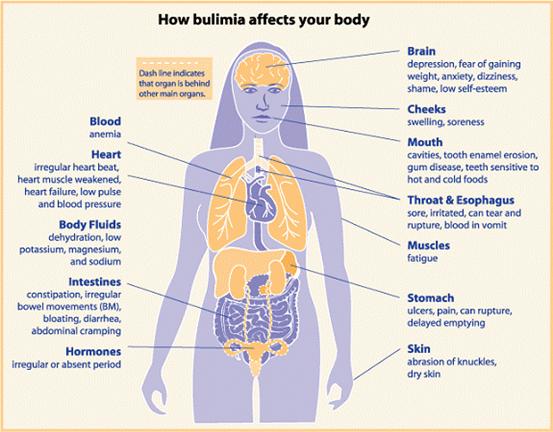
Moreover, bulimia can also lead to multiple severe conditions such as:
- kidney failure
- heart problems
- gum disease
- tooth decay
- digestive issues or constipation
- dehydration
- nutrient deficiencies
- electrolyte or chemical imbalances
Most women also go through the absence of their menstrual period and may experience mental difficulties such as anxiety, depression, drug abuse, etc.
The Causes of Bulimia
Even though Bulimia has no discrete cause, there are a couple of factors that can influence its development.
Especially, people with mental health disorders like the ones we covered in the previous guides; ADHD, Schizophrenia, etc. are at a higher risk. Other common factors include:
- anger issues
- depression
- perfectionism
- impulsiveness
- past traumatic event
Bulimia can also be passed down from generations, and hereditary. Moreover, it is also triggered by a serotonin deficiency in the brain, typically common in people with Cherophobia.
Diagnosis
To diagnose Bulimia, your doctor will conduct a series of tests on you. It can range from multiple physical tests to a blood and urine test as well.
Most doctors follow the criteria set by DSM-5; the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, this tool uses a standard criterion to accurately diagnose such disorders. The criteria used to diagnose bulimia includes:
- recurrent binge eating
- regular purging through vomiting
- persistent purging behaviors, like excessive exercising, misuse of laxatives, and fasting
- deriving self-worth from weight and body shape
- bingeing, purging, and purging behaviors that happen at least once a week for three months on average
- not having anorexia nervosa
Moreover, professionals determine the severity of your bulimia on how often you exhibit bingeing or related behaviors. The DSM-5 has generated categories for bulimia from mild to extreme which is as follows:
- mild: 1 to 3 episodes per week
- moderate: 4 to 7 episodes per week
- severe: 8 to 13 episodes per week
- extreme: 14 or more episodes per week
Treatment
The treatment process for bulimia not only focuses on the food and nutrition you ingest, but it also requires the patient to develop a healthy relationship with oneself and a healthy relationship with food.
Common treatment options include:
- Antidepressants, certain antidepressants are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat bulimia
- Psychotherapy, also called talk therapy, can include cognitive behavioral therapy, family-based therapy, and interpersonal psychotherapy
- Dietitian support and nutrition education, which means learning about healthy eating habits, forming a nutritious meal plan, and possibly a controlled weight loss program
- Treatment for complications, which may include hospitalization for severe cases of bulimia
Some patients require only limited treatments, some require all the above and extra attention as well. Bulimia depends on person to person and cannot be confined into one spectrum.
Life with Bulimia
If bulimia is not detected soon enough or accurately, it can be pretty dangerous. Bulimia is not only a physical condition, but it is also classified as a psychological condition. However, there is no need to lose hope.
Bulimia can be treated if the person is consistent with medication and therapy. Your weight does not define you- it does not determine your self-worth. We are all beautiful in our bodies, no matter how big or small, how broad, or narrow, we’re all meant to be loved.
Bulimia has a huge impact on one’s self-esteem and confidence because of the constant lack of serotonin and the negative body images in their mind. It is empirical to always be careful of what you to say others, to be humble, and to support one another no matter what.
About Us
Runway Pakistan is a complete solution provider for all your marketing communications related requirements. The ultimate hub of infotainment – Runway composes of all the key offerings – Monthly Print Magazine, Digital Magazine, Media Production, Creative Agency, PR Agency, and Marketing Consultancy that a brand needs to be seen, heard, and known!
Like and follow our Facebook page:
Runway Pakistan


